[ad_1]
Generative AI has been the largest expertise story of 2023. Virtually all people’s performed with ChatGPT, Steady Diffusion, GitHub Copilot, or Midjourney. A couple of have even tried out Bard or Claude, or run LLaMA1 on their laptop computer. And everybody has opinions about how these language fashions and artwork era packages are going to alter the character of labor, usher within the singularity, or even perhaps doom the human race. In enterprises, we’ve seen the whole lot from wholesale adoption to insurance policies that severely limit and even forbid the usage of generative AI.
What’s the truth? We needed to search out out what persons are truly doing, so in September we surveyed O’Reilly’s customers. Our survey targeted on how firms use generative AI, what bottlenecks they see in adoption, and what abilities gaps must be addressed.
Govt Abstract
We’ve by no means seen a expertise adopted as quick as generative AI—it’s exhausting to imagine that ChatGPT is barely a 12 months outdated. As of November 2023:
- Two-thirds (67%) of our survey respondents report that their firms are utilizing generative AI.
- AI customers say that AI programming (66%) and information evaluation (59%) are essentially the most wanted abilities.
- Many AI adopters are nonetheless within the early phases. 26% have been working with AI for below a 12 months. However 18% have already got functions in manufacturing.
- Problem discovering applicable use instances is the largest bar to adoption for each customers and nonusers.
- 16% of respondents working with AI are utilizing open supply fashions.
- Sudden outcomes, safety, security, equity and bias, and privateness are the largest dangers for which adopters are testing.
- 54% of AI customers count on AI’s largest profit shall be larger productiveness. Solely 4% pointed to decrease head counts.
Is generative AI on the prime of the hype curve? We see loads of room for development, notably as adopters uncover new use instances and reimagine how they do enterprise.
Customers and Nonusers
AI adoption is within the technique of turning into widespread, however it’s nonetheless not common. Two-thirds of our survey’s respondents (67%) report that their firms are utilizing generative AI. 41% say their firms have been utilizing AI for a 12 months or extra; 26% say their firms have been utilizing AI for lower than a 12 months. And solely 33% report that their firms aren’t utilizing AI in any respect.
Generative AI customers signify a two-to-one majority over nonusers, however what does that imply? If we requested whether or not their firms have been utilizing databases or internet servers, little doubt 100% of the respondents would have mentioned “sure.” Till AI reaches 100%, it’s nonetheless within the technique of adoption. ChatGPT was opened to the general public on November 30, 2022, roughly a 12 months in the past; the artwork turbines, resembling Steady Diffusion and DALL-E, are considerably older. A 12 months after the primary internet servers turned accessible, what number of firms had web sites or have been experimenting with constructing them? Actually not two-thirds of them. Trying solely at AI customers, over a 3rd (38%) report that their firms have been working with AI for lower than a 12 months and are nearly definitely nonetheless within the early phases: they’re experimenting and dealing on proof-of-concept initiatives. (We’ll say extra about this later.) Even with cloud-based basis fashions like GPT-4, which eradicate the necessity to develop your personal mannequin or present your personal infrastructure, fine-tuning a mannequin for any specific use case continues to be a serious endeavor. We’ve by no means seen adoption proceed so shortly.
When 26% of a survey’s respondents have been working with a expertise for below a 12 months, that’s an necessary signal of momentum. Sure, it’s conceivable that AI—and particularly generative AI—could possibly be on the peak of the hype cycle, as Gartner has argued. We don’t imagine that, despite the fact that the failure fee for a lot of of those new initiatives is undoubtedly excessive. However whereas the push to undertake AI has loads of momentum, AI will nonetheless need to show its worth to these new adopters, and shortly. Its adopters count on returns, and if not, nicely, AI has skilled many “winters” up to now. Are we on the prime of the adoption curve, with nowhere to go however down? Or is there nonetheless room for development?
We imagine there’s a variety of headroom. Coaching fashions and creating complicated functions on prime of these fashions is turning into simpler. Most of the new open supply fashions are a lot smaller and never as useful resource intensive however nonetheless ship good outcomes (particularly when educated for a particular software). Some can simply be run on a laptop computer and even in an internet browser. A wholesome instruments ecosystem has grown up round generative AI—and, as was mentioned in regards to the California Gold Rush, if you wish to see who’s making a living, don’t have a look at the miners; have a look at the folks promoting shovels. Automating the method of constructing complicated prompts has turn into frequent, with patterns like retrieval-augmented era (RAG) and instruments like LangChain. And there are instruments for archiving and indexing prompts for reuse, vector databases for retrieving paperwork that an AI can use to reply a query, and way more. We’re already transferring into the second (if not the third) era of tooling. A roller-coaster trip into Gartner’s “trough of disillusionment” is unlikely.
What’s Holding AI Again?
It was necessary for us to be taught why firms aren’t utilizing AI, so we requested respondents whose firms aren’t utilizing AI a single apparent query: “Why isn’t your organization utilizing AI?” We requested the same query to customers who mentioned their firms are utilizing AI: “What’s the primary bottleneck holding again additional AI adoption?” Each teams have been requested to pick from the identical group of solutions. The most typical motive, by a big margin, was issue discovering applicable enterprise use instances (31% for nonusers, 22% for customers). We may argue that this displays a scarcity of creativeness—however that’s not solely ungracious, it additionally presumes that making use of AI in every single place with out cautious thought is a good suggestion. The implications of “Transfer quick and break issues” are nonetheless enjoying out the world over, and it isn’t fairly. Badly thought-out and poorly applied AI options will be damaging, so most firms ought to think twice about use AI appropriately. We’re not encouraging skepticism or worry, however firms ought to begin AI merchandise with a transparent understanding of the dangers, particularly these dangers which are particular to AI. What use instances are applicable, and what aren’t? The flexibility to tell apart between the 2 is necessary, and it’s a difficulty for each firms that use AI and corporations that don’t. We even have to acknowledge that many of those use instances will problem conventional methods of fascinated by companies. Recognizing use instances for AI and understanding how AI means that you can reimagine the enterprise itself will go hand in hand.
The second commonest motive was concern about authorized points, danger, and compliance (18% for nonusers, 20% for customers). This fear definitely belongs to the identical story: danger must be thought of when fascinated by applicable use instances. The authorized penalties of utilizing generative AI are nonetheless unknown. Who owns the copyright for AI-generated output? Can the creation of a mannequin violate copyright, or is it a “transformative” use that’s protected below US copyright legislation? We don’t know proper now; the solutions shall be labored out within the courts within the years to come back. There are different dangers too, together with reputational injury when a mannequin generates inappropriate output, new safety vulnerabilities, and plenty of extra.
One other piece of the identical puzzle is the shortage of a coverage for AI use. Such insurance policies can be designed to mitigate authorized issues and require regulatory compliance. This isn’t as important a difficulty; it was cited by 6.3% of customers and three.9% of nonusers. Company insurance policies on AI use shall be showing and evolving over the subsequent 12 months. (At O’Reilly, we have now simply put our coverage for office use into place.) Late in 2023, we suspect that comparatively few firms have a coverage. And naturally, firms that don’t use AI don’t want an AI use coverage. Nevertheless it’s necessary to consider which is the cart and which is the horse. Does the shortage of a coverage stop the adoption of AI? Or are people adopting AI on their very own, exposing the corporate to unknown dangers and liabilities? Amongst AI customers, the absence of company-wide insurance policies isn’t holding again AI use; that’s self-evident. However this most likely isn’t factor. Once more, AI brings with it dangers and liabilities that must be addressed somewhat than ignored. Willful ignorance can solely result in unlucky penalties.
One other issue holding again the usage of AI is an organization tradition that doesn’t acknowledge the necessity (9.8% for nonusers, 6.7% for customers). In some respects, not recognizing the necessity is just like not discovering applicable enterprise use instances. However there’s additionally an necessary distinction: the phrase “applicable.” AI entails dangers, and discovering use instances which are applicable is a official concern. A tradition that doesn’t acknowledge the necessity is dismissive and will point out a scarcity of creativeness or forethought: “AI is only a fad, so we’ll simply proceed doing what has at all times labored for us.” Is that the problem? It’s exhausting to think about a enterprise the place AI couldn’t be put to make use of, and it could’t be wholesome to an organization’s long-term success to disregard that promise.
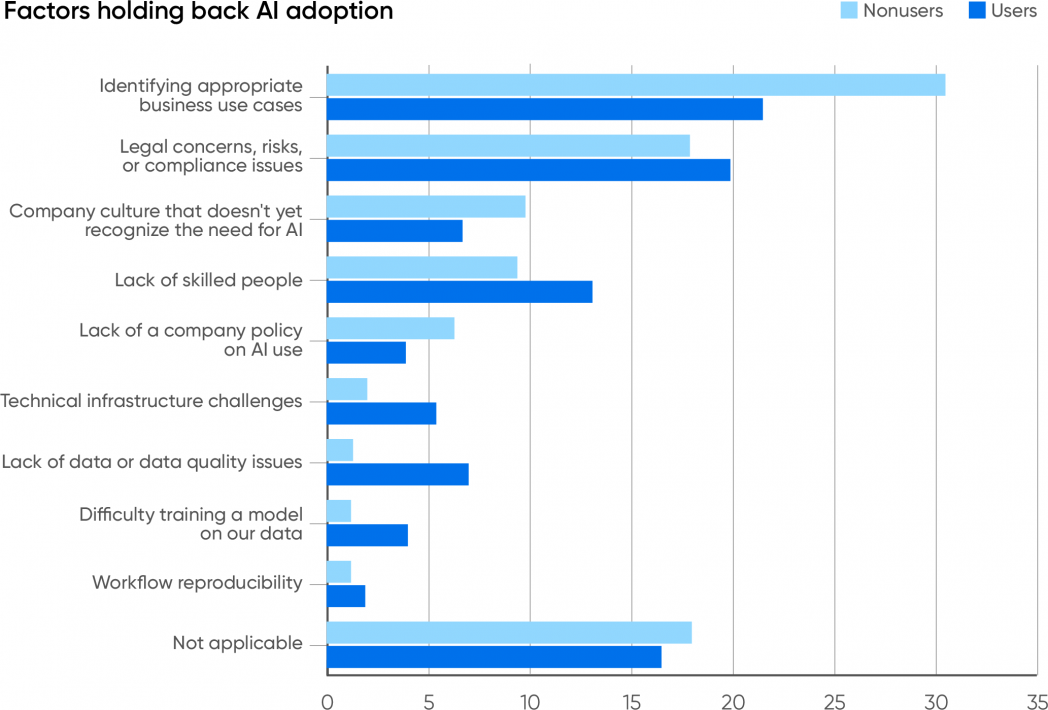
We’re sympathetic to firms that fear in regards to the lack of expert folks, a difficulty that was reported by 9.4% of nonusers and 13% of customers. Folks with AI abilities have at all times been exhausting to search out and are sometimes costly. We don’t count on that scenario to alter a lot within the close to future. Whereas skilled AI builders are beginning to depart powerhouses like Google, OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft, not sufficient are leaving to fulfill demand—and most of them will most likely gravitate to startups somewhat than including to the AI expertise inside established firms. Nonetheless, we’re additionally shocked that this problem doesn’t determine extra prominently. Firms which are adopting AI are clearly discovering employees someplace, whether or not by way of hiring or coaching their current employees.
A small proportion (3.7% of nonusers, 5.4% of customers) report that “infrastructure points” are a difficulty. Sure, constructing AI infrastructure is tough and costly, and it isn’t stunning that the AI customers really feel this downside extra keenly. We’ve all learn in regards to the scarcity of the high-end GPUs that energy fashions like ChatGPT. That is an space the place cloud suppliers already bear a lot of the burden, and can proceed to bear it sooner or later. Proper now, only a few AI adopters keep their very own infrastructure and are shielded from infrastructure points by their suppliers. In the long run, these points could sluggish AI adoption. We suspect that many API companies are being supplied as loss leaders—that the most important suppliers have deliberately set costs low to purchase market share. That pricing received’t be sustainable, notably as {hardware} shortages drive up the price of constructing infrastructure. How will AI adopters react when the price of renting infrastructure from AWS, Microsoft, or Google rises? Given the price of equipping an information heart with high-end GPUs, they most likely received’t try and construct their very own infrastructure. However they could again off on AI improvement.
Few nonusers (2%) report that lack of knowledge or information high quality is a matter, and just one.3% report that the issue of coaching a mannequin is an issue. In hindsight, this was predictable: these are issues that solely seem after you’ve began down the street to generative AI. AI customers are undoubtedly going through these issues: 7% report that information high quality has hindered additional adoption, and 4% cite the issue of coaching a mannequin on their information. However whereas information high quality and the issue of coaching a mannequin are clearly necessary points, they don’t look like the largest limitations to constructing with AI. Builders are studying discover high quality information and construct fashions that work.
How Firms Are Utilizing AI
We requested a number of particular questions on how respondents are working with AI, and whether or not they’re “utilizing” it or simply “experimenting.”
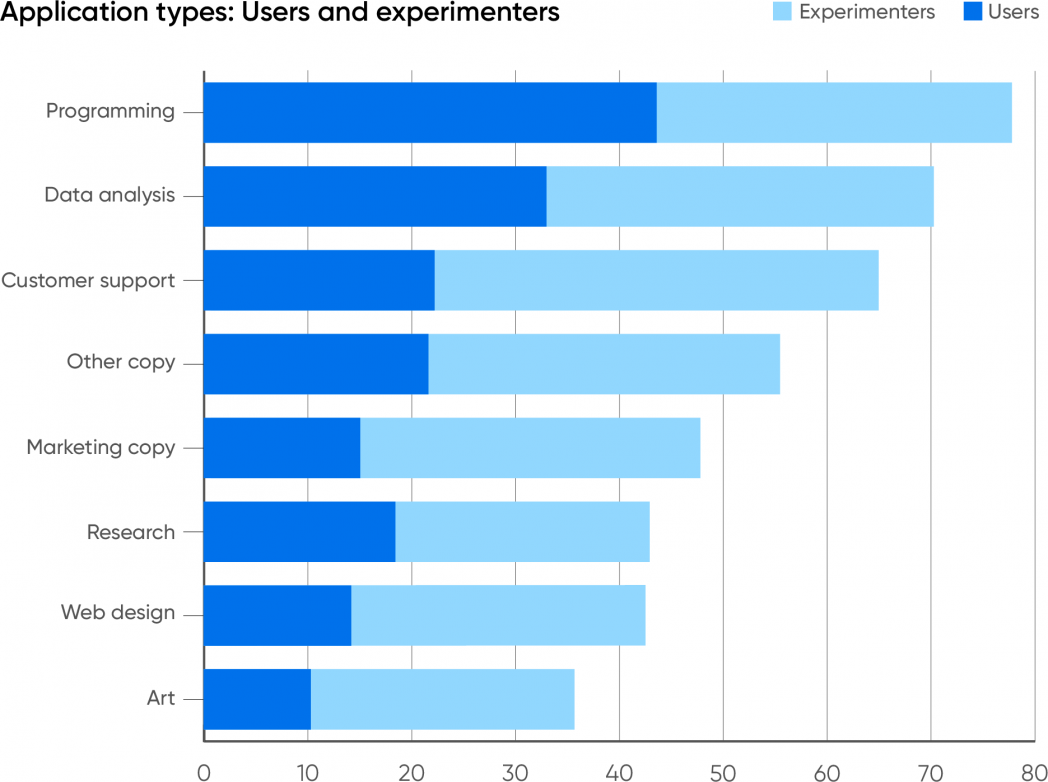
We aren’t shocked that the commonest software of generative AI is in programming, utilizing instruments like GitHub Copilot or ChatGPT. Nonetheless, we are shocked on the stage of adoption: 77% of respondents report utilizing AI as an assist in programming; 34% are experimenting with it, and 44% are already utilizing it of their work. Information evaluation confirmed the same sample: 70% whole; 32% utilizing AI, 38% experimenting with it. The upper proportion of customers which are experimenting could replicate OpenAI’s addition of Superior Information Evaluation (previously Code Interpreter) to ChatGPT’s repertoire of beta options. Superior Information Evaluation does an honest job of exploring and analyzing datasets—although we count on information analysts to watch out about checking AI’s output and to mistrust software program that’s labeled as “beta.”
Utilizing generative AI instruments for duties associated to programming (together with information evaluation) is sort of common. It can definitely turn into common for organizations that don’t explicitly prohibit its use. And we count on that programmers will use AI even in organizations that prohibit its use. Programmers have at all times developed instruments that may assist them do their jobs, from check frameworks to supply management to built-in improvement environments. And so they’ve at all times adopted these instruments whether or not or not that they had administration’s permission. From a programmer’s perspective, code era is simply one other labor-saving device that retains them productive in a job that’s always turning into extra complicated. Within the early 2000s, some research of open supply adoption discovered that a big majority of employees mentioned that they have been utilizing open supply, despite the fact that a big majority of CIOs mentioned their firms weren’t. Clearly these CIOs both didn’t know what their staff have been doing or have been keen to look the opposite approach. We’ll see that sample repeat itself: programmers will do what’s essential to get the job finished, and managers shall be blissfully unaware so long as their groups are extra productive and objectives are being met.
After programming and information evaluation, the subsequent commonest use for generative AI was functions that work together with clients, together with buyer assist: 65% of all respondents report that their firms are experimenting with (43%) or utilizing AI (22%) for this function. Whereas firms have lengthy been speaking about AI’s potential to enhance buyer assist, we didn’t count on to see customer support rank so excessive. Buyer-facing interactions are very dangerous: incorrect solutions, bigoted or sexist conduct, and plenty of different well-documented issues with generative AI shortly result in injury that’s exhausting to undo. Maybe that’s why such a big proportion of respondents are experimenting with this expertise somewhat than utilizing it (greater than for some other type of software). Any try at automating customer support must be very rigorously examined and debugged. We interpret our survey outcomes as “cautious however excited adoption.” It’s clear that automating customer support may go a protracted method to lower prices and even, if finished nicely, make clients happier. Nobody needs to be left behind, however on the similar time, nobody needs a extremely seen PR catastrophe or a lawsuit on their fingers.
A reasonable variety of respondents report that their firms are utilizing generative AI to generate copy (written textual content). 47% are utilizing it particularly to generate advertising copy, and 56% are utilizing it for different kinds of copy (inner memos and reviews, for instance). Whereas rumors abound, we’ve seen few reviews of people that have truly misplaced their jobs to AI—however these reviews have been nearly completely from copywriters. AI isn’t but on the level the place it could write in addition to an skilled human, but when your organization wants catalog descriptions for lots of of things, pace could also be extra necessary than good prose. And there are various different functions for machine-generated textual content: AI is sweet at summarizing paperwork. When coupled with a speech-to-text service, it could do a satisfactory job of making assembly notes and even podcast transcripts. It’s additionally nicely suited to writing a fast e-mail.
The functions of generative AI with the fewest customers have been internet design (42% whole; 28% experimenting, 14% utilizing) and artwork (36% whole; 25% experimenting, 11% utilizing). This little doubt displays O’Reilly’s developer-centric viewers. Nonetheless, a number of different elements are in play. First, there are already a variety of low-code and no-code internet design instruments, lots of which function AI however aren’t but utilizing generative AI. Generative AI will face important entrenched competitors on this crowded market. Second, whereas OpenAI’s GPT-4 announcement final March demoed producing web site code from a hand-drawn sketch, that functionality wasn’t accessible till after the survey closed. Third, whereas roughing out the HTML and JavaScript for a easy web site makes an important demo, that isn’t actually the issue internet designers want to unravel. They need a drag-and-drop interface that may be edited on-screen, one thing that generative AI fashions don’t but have. These functions shall be constructed quickly; tldraw is a really early instance of what they may be. Design instruments appropriate for skilled use don’t exist but, however they are going to seem very quickly.
A fair smaller proportion of respondents say that their firms are utilizing generative AI to create artwork. Whereas we’ve examine startup founders utilizing Steady Diffusion and Midjourney to create firm or product logos on a budget, that’s nonetheless a specialised software and one thing you don’t do often. However that isn’t all of the artwork that an organization wants: “hero photos” for weblog posts, designs for reviews and whitepapers, edits to publicity pictures, and extra are all crucial. Is generative AI the reply? Maybe not but. Take Midjourneyfor instance: whereas its capabilities are spectacular, the device also can make foolish errors, like getting the variety of fingers (or arms) on topics incorrect. Whereas the newest model of Midjourney is significantly better, it hasn’t been out for lengthy, and plenty of artists and designers would like to not cope with the errors. They’d additionally choose to keep away from authorized legal responsibility. Amongst generative artwork distributors, Shutterstock, Adobe, and Getty Photographs indemnify customers of their instruments towards copyright claims. Microsoft, Google, IBM, and OpenAI have supplied extra normal indemnification.
We additionally requested whether or not the respondents’ firms are utilizing AI to create another type of software, and if that’s the case, what. Whereas many of those write-in functions duplicated options already accessible from large AI suppliers like Microsoft, OpenAI, and Google, others lined a really spectacular vary. Most of the functions concerned summarization: information, authorized paperwork and contracts, veterinary medication, and monetary info stand out. A number of respondents additionally talked about working with video: analyzing video information streams, video analytics, and producing or enhancing movies.
Different functions that respondents listed included fraud detection, educating, buyer relations administration, human assets, and compliance, together with extra predictable functions like chat, code era, and writing. We are able to’t tally and tabulate all of the responses, however it’s clear that there’s no scarcity of creativity and innovation. It’s additionally clear that there are few industries that received’t be touched—AI will turn into an integral a part of nearly each career.
Generative AI will take its place as the final word workplace productiveness device. When this occurs, it could now not be acknowledged as AI; it is going to simply be a function of Microsoft Workplace or Google Docs or Adobe Photoshop, all of that are integrating generative AI fashions. GitHub Copilot and Google’s Codey have each been built-in into Microsoft and Google’s respective programming environments. They may merely be a part of the setting during which software program builders work. The identical factor occurred to networking 20 or 25 years in the past: wiring an workplace or a home for ethernet was once a giant deal. Now we count on wi-fi in every single place, and even that’s not appropriate. We don’t “count on” it—we assume it, and if it’s not there, it’s an issue. We count on cellular to be in every single place, together with map companies, and it’s an issue in case you get misplaced in a location the place the cell alerts don’t attain. We count on search to be in every single place. AI would be the similar. It received’t be anticipated; will probably be assumed, and an necessary a part of the transition to AI in every single place shall be understanding work when it isn’t accessible.
The Builders and Their Instruments
To get a special tackle what our clients are doing with AI, we requested what fashions they’re utilizing to construct customized functions. 36% indicated that they aren’t constructing a customized software. As an alternative, they’re working with a prepackaged software like ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, the AI options built-in into Microsoft Workplace and Google Docs, or one thing related. The remaining 64% have shifted from utilizing AI to creating AI functions. This transition represents a giant leap ahead: it requires funding in folks, in infrastructure, and in schooling.
Which Mannequin?
Whereas the GPT fashions dominate a lot of the on-line chatter, the variety of fashions accessible for constructing functions is growing quickly. We examine a brand new mannequin nearly day-after-day—definitely each week—and a fast have a look at Hugging Face will present you extra fashions than you’ll be able to depend. (As of November, the variety of fashions in its repository is approaching 400,000.) Builders clearly have decisions. However what decisions are they making? Which fashions are they utilizing?
It’s no shock that 23% of respondents report that their firms are utilizing one of many GPT fashions (2, 3.5, 4, and 4V), greater than some other mannequin. It’s an even bigger shock that 21% of respondents are creating their very own mannequin; that process requires substantial assets in employees and infrastructure. It will likely be value watching how this evolves: will firms proceed to develop their very own fashions, or will they use AI companies that enable a basis mannequin (like GPT-4) to be personalized?
16% of the respondents report that their firms are constructing on prime of open supply fashions. Open supply fashions are a big and various group. One necessary subsection consists of fashions derived from Meta’s LLaMA: llama.cpp, Alpaca, Vicuna, and plenty of others. These fashions are sometimes smaller (7 to 14 billion parameters) and simpler to fine-tune, and so they can run on very restricted {hardware}; many can run on laptops, cell telephones, or nanocomputers such because the Raspberry Pi. Coaching requires way more {hardware}, however the means to run in a restricted setting signifies that a completed mannequin will be embedded inside a {hardware} or software program product. One other subsection of fashions has no relationship to LLaMA: RedPajama, Falcon, MPT, Bloom, and plenty of others, most of which can be found on Hugging Face. The variety of builders utilizing any particular mannequin is comparatively small, however the whole is spectacular and demonstrates a significant and lively world past GPT. These “different” fashions have attracted a big following. Watch out, although: whereas this group of fashions is often known as “open supply,” lots of them limit what builders can construct from them. Earlier than working with any so-called open supply mannequin, look rigorously on the license. Some restrict the mannequin to analysis work and prohibit industrial functions; some prohibit competing with the mannequin’s builders; and extra. We’re caught with the time period “open supply” for now, however the place AI is worried, open supply typically isn’t what it appears to be.
Solely 2.4% of the respondents are constructing with LLaMA and Llama 2. Whereas the supply code and weights for the LLaMA fashions can be found on-line, the LLaMA fashions don’t but have a public API backed by Meta—though there look like a number of APIs developed by third events, and each Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure provide Llama 2 as a service. The LLaMA-family fashions additionally fall into the “so-called open supply” class that restricts what you’ll be able to construct.
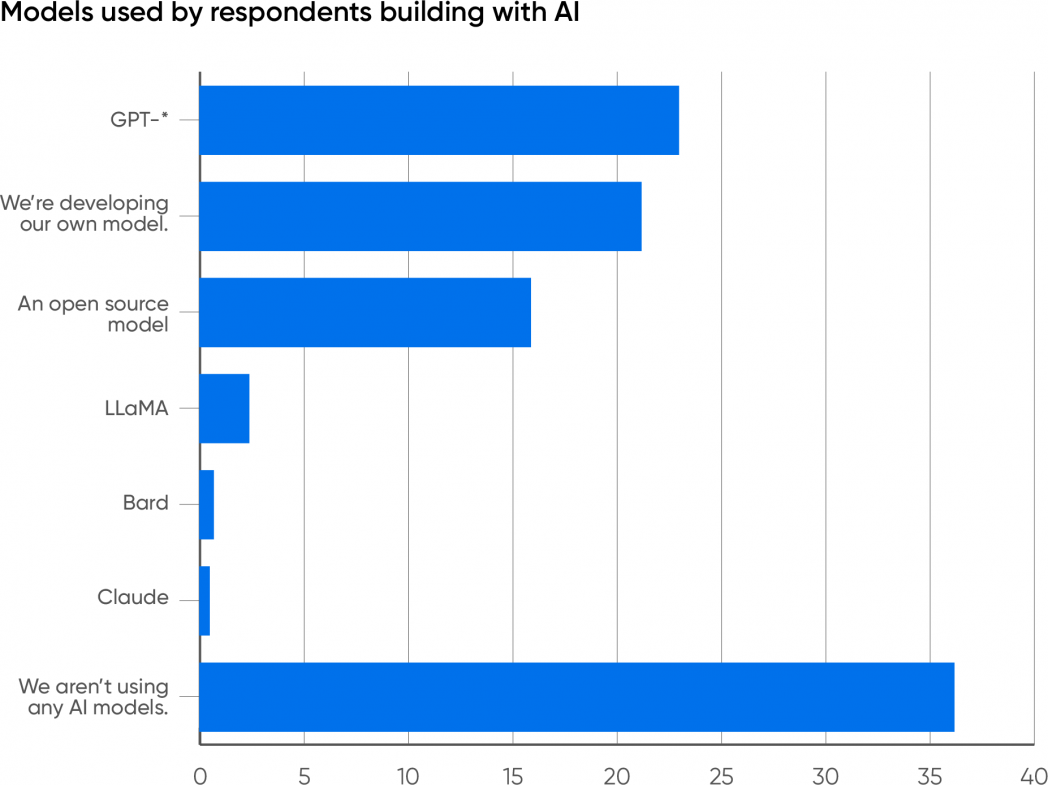
Just one% are constructing with Google’s Bard, which maybe has much less publicity than the others. Quite a lot of writers have claimed that Bard offers worse outcomes than the LLaMA and GPT fashions; that could be true for chat, however I’ve discovered that Bard is commonly appropriate when GPT-4 fails. For app builders, the largest downside with Bard most likely isn’t accuracy or correctness; it’s availability. In March 2023, Google introduced a public beta program for the Bard API. Nonetheless, as of November, questions on API availability are nonetheless answered by hyperlinks to the beta announcement. Use of the Bard API is undoubtedly hampered by the comparatively small variety of builders who’ve entry to it. Even fewer are utilizing Claude, a really succesful mannequin developed by Anthropic. Claude doesn’t get as a lot information protection because the fashions from Meta, OpenAI, and Google, which is unlucky: Anthropic’s Constitutional AI strategy to AI security is a novel and promising try to unravel the largest issues troubling the AI trade.
What Stage?
When requested what stage firms are at of their work, most respondents shared that they’re nonetheless within the early phases. Provided that generative AI is comparatively new, that isn’t information. If something, we must be shocked that generative AI has penetrated so deeply and so shortly. 34% of respondents are engaged on an preliminary proof of idea. 14% are in product improvement, presumably after creating a PoC; 10% are constructing a mannequin, additionally an early stage exercise; and eight% are testing, which presumes that they’ve already constructed a proof of idea and are transferring towards deployment—they’ve a mannequin that not less than seems to work.
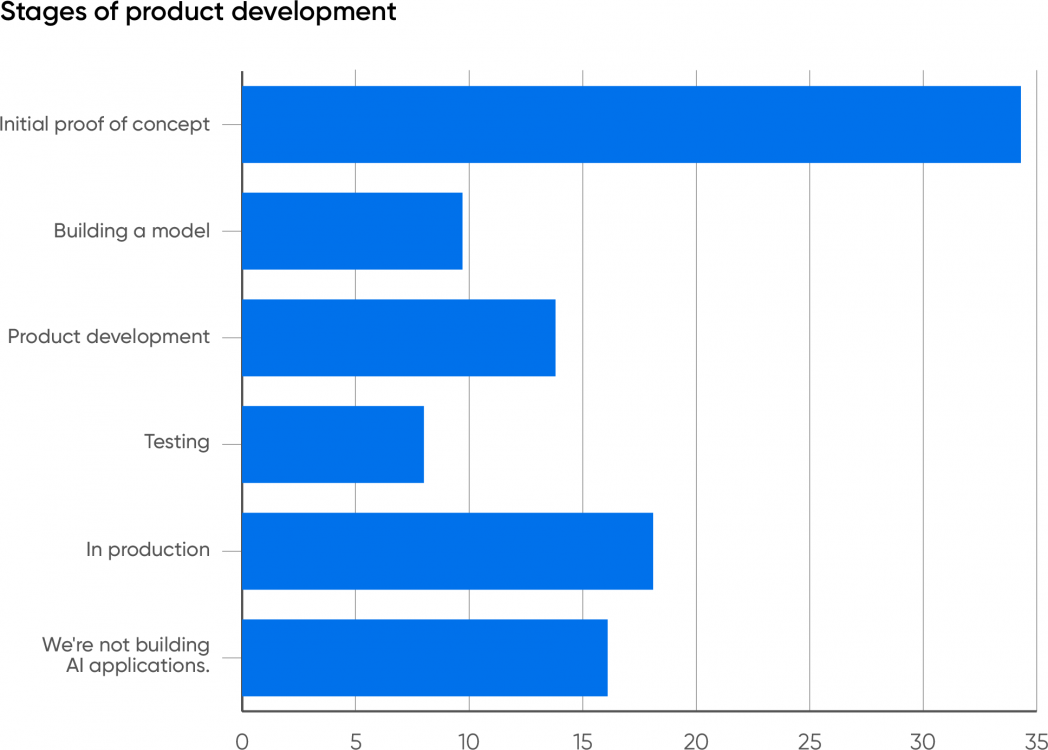
What stands out is that 18% of the respondents work for firms which have AI functions in manufacturing. Provided that the expertise is new and that many AI initiatives fail,2 it’s stunning that 18% report that their firms have already got generative AI functions in manufacturing. We’re not being skeptics; that is proof that whereas most respondents report firms which are engaged on proofs of idea or in different early phases, generative AI is being adopted and is doing actual work. We’ve already seen some important integrations of AI into current merchandise, together with our personal. We count on others to comply with.
Dangers and Checks
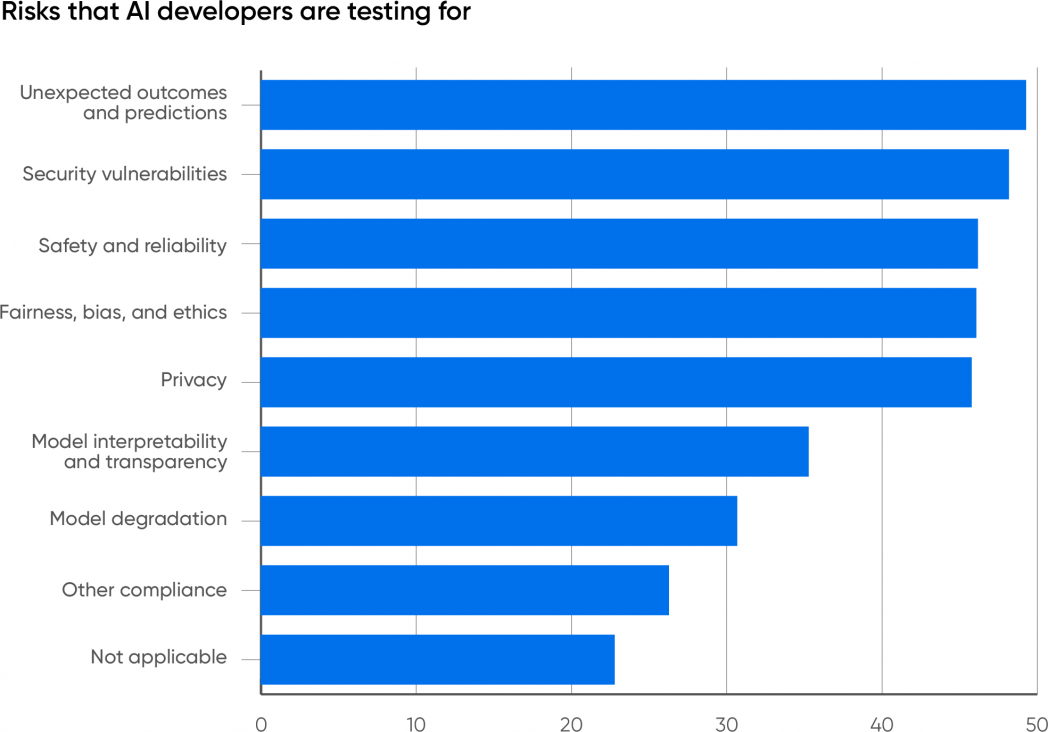
We requested the respondents whose firms are working with AI what dangers they’re testing for. The highest 5 responses clustered between 45 and 50%: sudden outcomes (49%), safety vulnerabilities (48%), security and reliability (46%), equity, bias, and ethics (46%), and privateness (46%).
It’s necessary that just about half of respondents chosen “sudden outcomes,” greater than some other reply: anybody working with generative AI must know that incorrect outcomes (typically known as hallucinations) are frequent. If there’s a shock right here, it’s that this reply wasn’t chosen by 100% of the members. Sudden, incorrect, or inappropriate outcomes are nearly definitely the largest single danger related to generative AI.
We’d wish to see extra firms check for equity. There are a lot of functions (for instance, medical functions) the place bias is among the many most necessary issues to check for and the place eliminating historic biases within the coaching information could be very tough and of utmost significance. It’s necessary to understand that unfair or biased output will be very delicate, notably if software builders don’t belong to teams that have bias—and what’s “delicate” to a developer is commonly very unsubtle to a person. A chat software that doesn’t perceive a person’s accent is an apparent downside (seek for “Amazon Alexa doesn’t perceive Scottish accent”). It’s additionally necessary to search for functions the place bias isn’t a difficulty. ChatGPT has pushed a give attention to private use instances, however there are various functions the place issues of bias and equity aren’t main points: for instance, inspecting photos to inform whether or not crops are diseased or optimizing a constructing’s heating and air-con for optimum effectivity whereas sustaining consolation.
It’s good to see points like security and safety close to the highest of the record. Firms are steadily waking as much as the concept safety is a severe problem, not only a value heart. In lots of functions (for instance, customer support), generative AI is able to do important reputational injury, along with creating authorized legal responsibility. Moreover, generative AI has its personal vulnerabilities, resembling immediate injection, for which there’s nonetheless no recognized resolution. Mannequin leeching, during which an attacker makes use of specifically designed prompts to reconstruct the information on which the mannequin was educated, is one other assault that’s distinctive to AI. Whereas 48% isn’t dangerous, we want to see even larger consciousness of the necessity to check AI functions for safety.
Mannequin interpretability (35%) and mannequin degradation (31%) aren’t as large issues. Sadly, interpretability stays a analysis downside for generative AI. A minimum of with the present language fashions, it’s very tough to clarify why a generative mannequin gave a particular reply to any query. Interpretability won’t be a requirement for many present functions. If ChatGPT writes a Python script for you, you could not care why it wrote that exact script somewhat than one thing else. (It’s additionally value remembering that in case you ask ChatGPT why it produced any response, its reply is not going to be the rationale for the earlier response, however, as at all times, the most certainly response to your query.) However interpretability is important for diagnosing issues of bias and shall be extraordinarily necessary when instances involving generative AI find yourself in courtroom.
Mannequin degradation is a special concern. The efficiency of any AI mannequin degrades over time, and so far as we all know, giant language fashions aren’t any exception. One hotly debated examine argues that the standard of GPT-4’s responses has dropped over time. Language modifications in delicate methods; the questions customers ask shift and might not be answerable with older coaching information. Even the existence of an AI answering questions may trigger a change in what questions are requested. One other fascinating problem is what occurs when generative fashions are educated on information generated by different generative fashions. Is “mannequin collapse” actual, and what affect will it have as fashions are retrained?
If you happen to’re merely constructing an software on prime of an current mannequin, you could not be capable to do something about mannequin degradation. Mannequin degradation is a a lot greater problem for builders who’re constructing their very own mannequin or doing further coaching to fine-tune an current mannequin. Coaching a mannequin is pricey, and it’s prone to be an ongoing course of.
Lacking Abilities
One of many largest challenges going through firms creating with AI is experience. Have they got employees with the mandatory abilities to construct, deploy, and handle these functions? To search out out the place the talents deficits are, we requested our respondents what abilities their organizations want to accumulate for AI initiatives. We weren’t shocked that AI programming (66%) and information evaluation (59%) are the 2 most wanted. AI is the subsequent era of what we known as “information science” a number of years again, and information science represented a merger between statistical modeling and software program improvement. The sphere could have developed from conventional statistical evaluation to synthetic intelligence, however its general form hasn’t modified a lot.
The subsequent most wanted talent is operations for AI and ML (54%). We’re glad to see folks acknowledge this; we’ve lengthy thought that operations was the “elephant within the room” for AI and ML. Deploying and managing AI merchandise isn’t easy. These merchandise differ in some ways from extra conventional functions, and whereas practices like steady integration and deployment have been very efficient for conventional software program functions, AI requires a rethinking of those code-centric methodologies. The mannequin, not the supply code, is an important a part of any AI software, and fashions are giant binary information that aren’t amenable to supply management instruments like Git. And in contrast to supply code, fashions develop stale over time and require fixed monitoring and testing. The statistical conduct of most fashions signifies that easy, deterministic testing received’t work; you’ll be able to’t assure that, given the identical enter, a mannequin will generate the identical output. The result’s that AI operations is a specialty of its personal, one which requires a deep understanding of AI and its necessities along with extra conventional operations. What sorts of deployment pipelines, repositories, and check frameworks do we have to put AI functions into manufacturing? We don’t know; we’re nonetheless creating the instruments and practices wanted to deploy and handle AI efficiently.
Infrastructure engineering, a selection chosen by 45% of respondents, doesn’t rank as excessive. This can be a little bit of a puzzle: working AI functions in manufacturing can require big assets, as firms as giant as Microsoft are discovering out. Nonetheless, most organizations aren’t but working AI on their very own infrastructure. They’re both utilizing APIs from an AI supplier like OpenAI, Microsoft, Amazon, or Google or they’re utilizing a cloud supplier to run a homegrown software. However in each instances, another supplier builds and manages the infrastructure. OpenAI particularly affords enterprise companies, which incorporates APIs for coaching customized fashions together with stronger ensures about protecting company information non-public. Nonetheless, with cloud suppliers working close to full capability, it is smart for firms investing in AI to start out fascinated by their very own infrastructure and buying the capability to construct it.
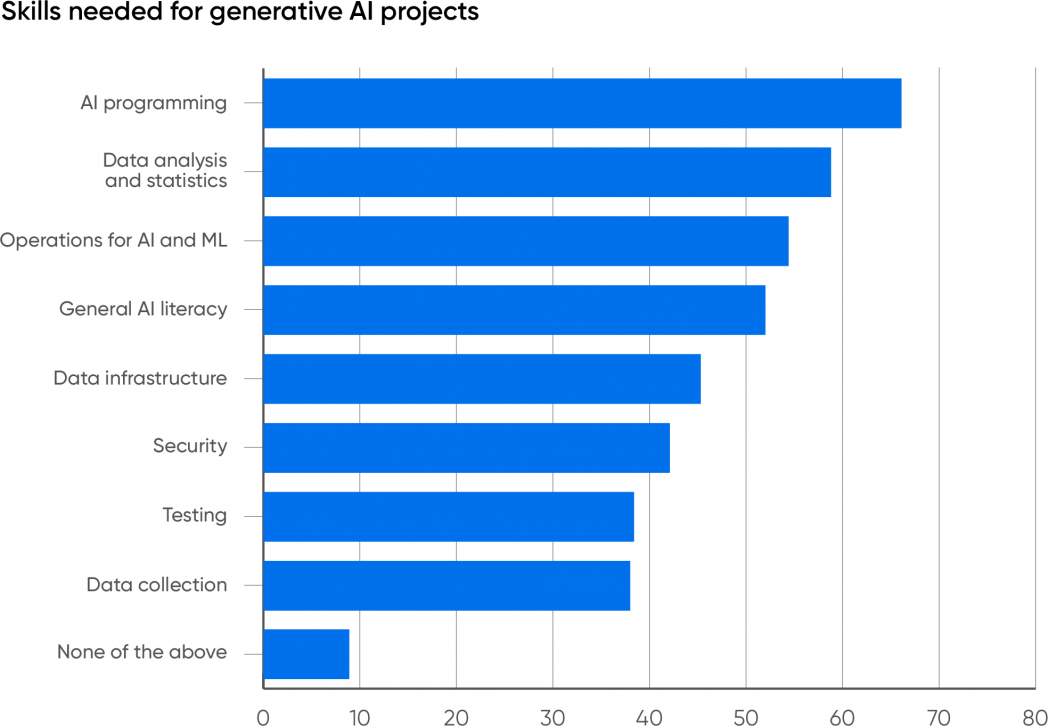
Over half of the respondents (52%) included normal AI literacy as a wanted talent. Whereas the quantity could possibly be larger, we’re glad that our customers acknowledge that familiarity with AI and the way in which AI methods behave (or misbehave) is important. Generative AI has an important wow issue: with a easy immediate, you will get ChatGPT to let you know about Maxwell’s equations or the Peloponnesian Struggle. However easy prompts don’t get you very far in enterprise. AI customers quickly be taught that good prompts are sometimes very complicated, describing intimately the outcome they need and get it. Prompts will be very lengthy, and so they can embrace all of the assets wanted to reply the person’s query. Researchers debate whether or not this stage of immediate engineering shall be crucial sooner or later, however it is going to clearly be with us for the subsequent few years. AI customers additionally have to count on incorrect solutions and to be geared up to examine nearly all of the output that an AI produces. That is typically known as important pondering, however it’s way more just like the technique of discovery in legislation: an exhaustive search of all doable proof. Customers additionally have to know create a immediate for an AI system that may generate a helpful reply.
Lastly, the Enterprise
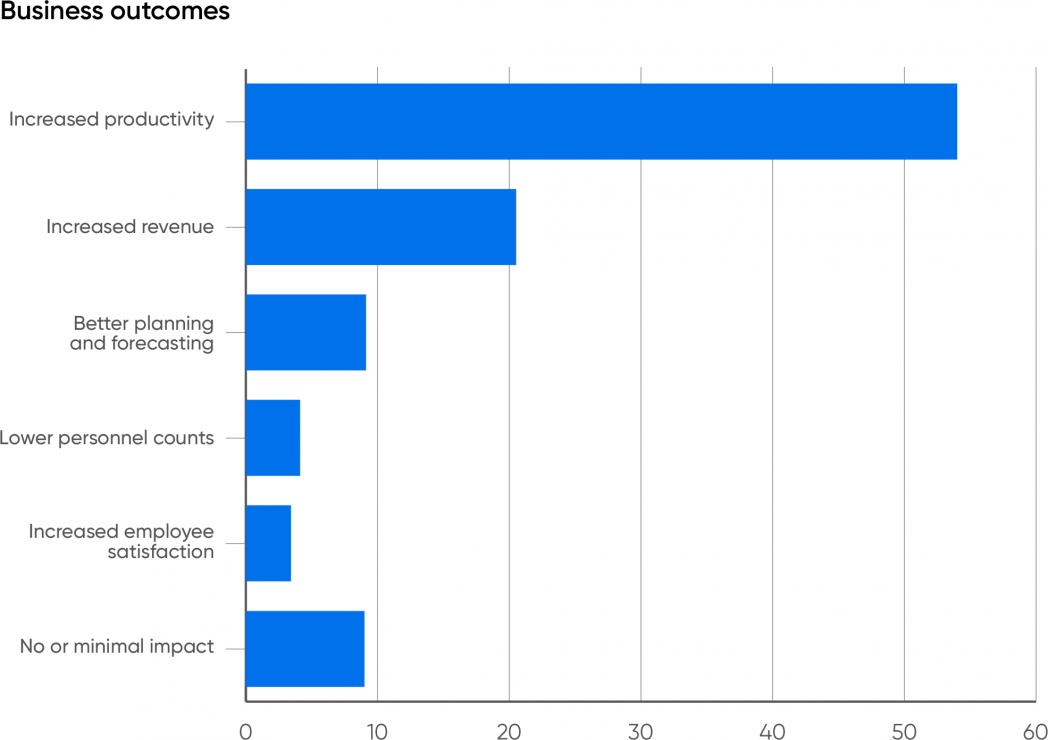
So what’s the underside line? How do companies profit from AI? Over half (54%) of the respondents count on their companies to learn from elevated productiveness. 21% count on elevated income, which could certainly be the results of elevated productiveness. Collectively, that’s three-quarters of the respondents. One other 9% say that their firms would profit from higher planning and forecasting.
Solely 4% imagine that the first profit shall be decrease personnel counts. We’ve lengthy thought that the worry of shedding your job to AI was exaggerated. Whereas there shall be some short-term dislocation as a number of jobs turn into out of date, AI will even create new jobs—as has nearly each important new expertise, together with computing itself. Most jobs depend on a large number of particular person abilities, and generative AI can solely substitute for a number of of them. Most staff are additionally keen to make use of instruments that may make their jobs simpler, boosting productiveness within the course of. We don’t imagine that AI will exchange folks, and neither do our respondents. However, staff will want coaching to make use of AI-driven instruments successfully, and it’s the accountability of the employer to supply that coaching.
We’re optimistic about generative AI’s future. It’s exhausting to understand that ChatGPT has solely been round for a 12 months; the expertise world has modified a lot in that quick interval. We’ve by no means seen a brand new expertise command a lot consideration so shortly: not private computer systems, not the web, not the online. It’s definitely doable that we’ll slide into one other AI winter if the investments being made in generative AI don’t pan out. There are undoubtedly issues that must be solved—correctness, equity, bias, and safety are among the many largest—and a few early adopters will ignore these hazards and undergo the implications. However, we imagine that worrying a couple of normal AI deciding that people are pointless is both an affliction of those that learn an excessive amount of science fiction or a technique to encourage regulation that offers the present incumbents a bonus over startups.
It’s time to start out studying about generative AI, fascinated by the way it can enhance your organization’s enterprise, and planning a technique. We are able to’t let you know what to do; builders are pushing AI into nearly each side of enterprise. However firms might want to put money into coaching, each for software program builders and for AI customers; they’ll have to put money into the assets required to develop and run functions, whether or not within the cloud or in their very own information facilities; and so they’ll have to assume creatively about how they’ll put AI to work, realizing that the solutions might not be what they count on.
AI received’t exchange people, however firms that reap the benefits of AI will exchange firms that don’t.
Footnotes
- Meta has dropped the odd capitalization for Llama 2. On this report, we use LLaMA to confer with the LLaMA fashions generically: LLaMA, Llama 2, and Llama n, when future variations exist. Though capitalization modifications, we use Claude to refer each to the unique Claude and to Claude 2, and Bard to Google’s Bard mannequin and its successors.
- Many articles quote Gartner as saying that the failure fee for AI initiatives is 85%. We haven’t discovered the supply, although in 2018, Gartner wrote that 85% of AI initiatives “ship inaccurate outcomes.” That’s not the identical as failure, and 2018 considerably predates generative AI. Generative AI is definitely susceptible to “inaccurate outcomes,” and we suspect the failure fee is excessive. 85% may be an affordable estimate.
Appendix
Methodology and Demographics
This survey ran from September 14, 2023, to September 27, 2023. It was publicized by way of O’Reilly’s studying platform to all our customers, each company and people. We obtained 4,782 responses, of which 2,857 answered all of the questions. As we often do, we eradicated incomplete responses (customers who dropped out half approach by way of the questions). Respondents who indicated they weren’t utilizing generative AI have been requested a remaining query about why they weren’t utilizing it, and regarded full.
Any survey solely offers a partial image, and it’s essential to consider biases. The largest bias by far is the character of O’Reilly’s viewers, which is predominantly North American and European. 42% of the respondents have been from North America, 32% have been from Europe, and 21% p.c have been from the Asia-Pacific area. Comparatively few respondents have been from South America or Africa, though we’re conscious of very fascinating functions of AI on these continents.
The responses are additionally skewed by the industries that use our platform most closely. 34% of all respondents who accomplished the survey have been from the software program trade, and one other 11% labored on pc {hardware}, collectively making up nearly half of the respondents. 14% have been in monetary companies, which is one other space the place our platform has many customers. 5% of the respondents have been from telecommunications, 5% from the general public sector and the federal government, 4.4% from the healthcare trade, and three.7% from schooling. These are nonetheless wholesome numbers: there have been over 100 respondents in every group. The remaining 22% represented different industries, starting from mining (0.1%) and development (0.2%) to manufacturing (2.6%).
These percentages change little or no in case you look solely at respondents whose employers use AI somewhat than all respondents who accomplished the survey. This means that AI utilization doesn’t rely rather a lot on the precise trade; the variations between industries displays the inhabitants of O’Reilly’s person base.
[ad_2]

