[ad_1]
There are a lot of variations of canine tumors and never all are created equal. Some tumors are much less problematic for canines, whereas others danger spreading all through the physique. Understanding widespread sorts of tumors, how they current and are handled, and signs to observe for, is important in early remedy and intervention.
Two major sorts of canine tumors
Tumors are characterised as both benign or malignant:
Benign tumors are noncancerous tumors that won’t unfold all through the physique.
Malignant tumors are cancerous and have the power to unfold most cancers all through your canine’s physique. Early intervention is a key part to remedy and restoration.
Widespread tumors in canines embody:
- Lipoma.Benign, fatty tumors that are typically gentle and cellular (not hooked up to your canine’s physique wall) and vary in dimension.
- Mast cell tumor (MCT). Malignant tumors that usually appear to be warts or bug bites and may change in dimension. MCTs are mostly seen in Boxers, Boston Terriers, Bull Terriers, and Pugs.
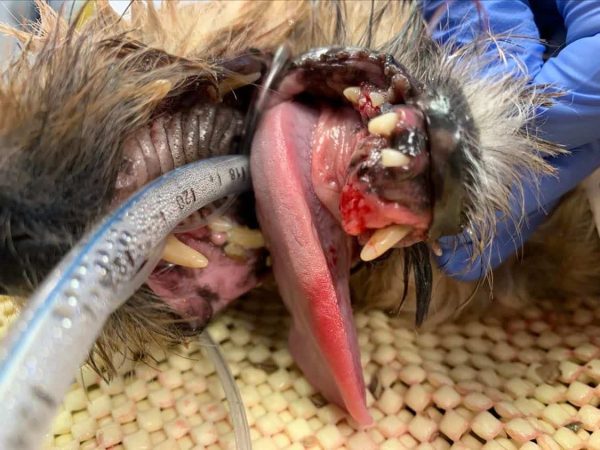
- Papilloma.Wart-like, viral tumors that sometimes seem in or round a canine’s mouth. Papillomas are benign however contagious between canines and are sometimes characterised as whitish lots with cauliflower texture.
- Histiocytoma. A quick rising, benign tumor sometimes present in younger canines. These tumors are identified for an infection and ulceration, nevertheless are likely to resolve on their very own with time.
- Hemangiosarcoma. A extremely malignant tumor stemming from blood vessels. This tumor usually impacts the liver, pores and skin and spleen and generally impacts senior pups.
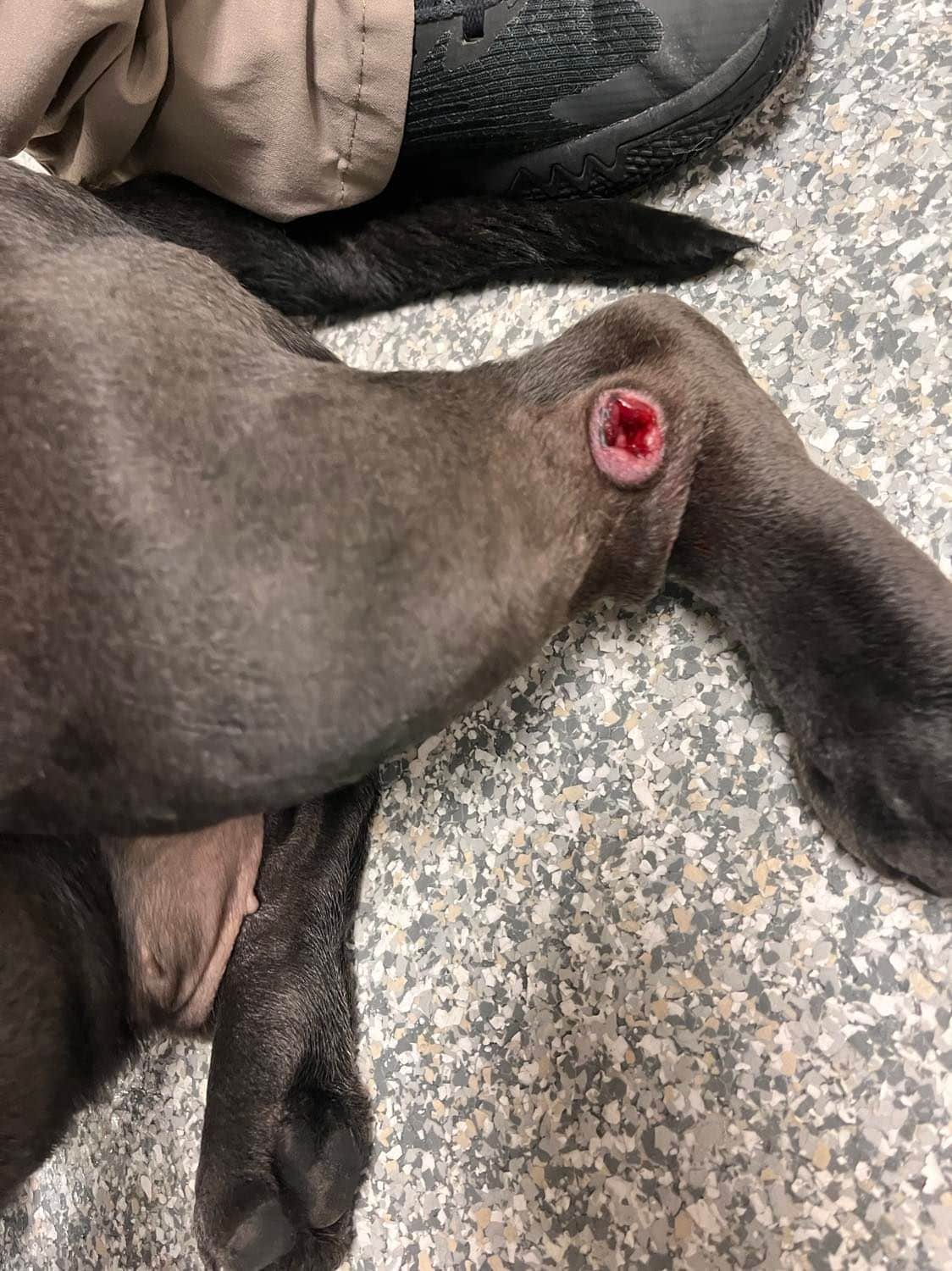
- Osteosarcoma. Malignant tumor of the bones, osteosarcoma causes vital ache, usually affecting a forelimb.
- Melanoma. Malignant tumors usually discovered within the oral cavity of canines and might be very aggressive. There’s now a melanoma vaccine accessible to canines identified with this tumor!
- Sebaceous gland tumor. Raised nodules that originate from sebaceous glands. In uncommon instances, sebaceous cysts develop into malignant. Keep in mind that no tumor ought to go unmonitored or forgotten!
Signs
Canine tumor signs will fluctuate vastly relying on many components and should embody:
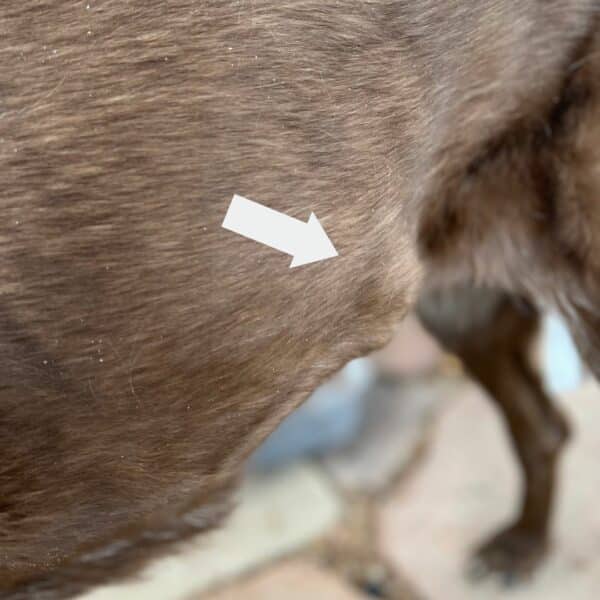
- Visualizing a lump or bump
- Limping
- Ache
- Low urge for food
- Problem consuming
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Coughing
- Weight reduction
In case your canine reveals any of those signs, go to your veterinarian.
Prognosis
The most typical methods to diagnose canine tumors embody:
- High quality needle aspirate (FNA). A positive needle aspirate (FNA) includes accumulating samples of cells out of your canine’s tumor utilizing a needle and syringe and viewing these cells microscopically.
- A biopsy includes accumulating and submitting a small quantity of the tumor for pathology assessment. A biopsy reveals detailed details about the tumor and may also help to stage malignant tumors.
Your veterinarian could suggest extra testing akin to radiographs, stomach ultrasound or a lymph node biopsy.
Therapy
Treating malignant tumors could embody:
- Surgical removing
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
- Palliative or hospice care
Treating benign tumors could embody:
- Surgical removing
- Managing an infection
- Lifelong monitoring
Early detection at dwelling
Benign tumors ought to stay intently monitored by you and your veterinary crew. If modifications happen in dimension, form or consistency, have them reassessed. Common exams by your veterinarian are key find tumors much less seen to the bare eye.
Early detection of malignant tumors usually occurs at dwelling. Often massaging your canine may also help you retain tabs on present and new tumors. Monitor modifications in your canine’s on a regular basis habits and take heed to your intestine. You might be your canine’s largest medical advocate!
[ad_2]