[ad_1]
Writer and Web page info
- This web page: https://www.globalissues.org/article/35/foreign-aid-development-assistance.
- To print all info (e.g. expanded aspect notes, reveals different hyperlinks), use the print model:
International assist or (growth help) is usually thought to be being an excessive amount of, or wasted on corrupt recipient governments regardless of any good intentions from donor international locations. In actuality, each the amount and high quality of assist have been poor and donor nations haven’t been held to account.
There are quite a few types of assist, from humanitarian emergency help, to meals assist, navy help, and many others. Improvement assist has lengthy been acknowledged as essential to assist poor growing nations develop out of poverty.
In 1970, the world’s wealthy international locations agreed to offer 0.7% of their GNI (Gross Nationwide Earnings) as official worldwide growth assist, yearly. Since that point, regardless of billions given annually, wealthy nations have hardly ever met their precise promised targets. For instance, the US is usually the most important donor in greenback phrases, however ranks amongst the bottom by way of assembly the said 0.7% goal.
Moreover, assist has typically include a value of its personal for the growing nations:
- Help is usually wasted on situations that the recipient should use overpriced items and companies from donor international locations
- Most assist doesn’t really go to the poorest who would want it essentially the most
- Help quantities are dwarfed by wealthy nation protectionism that denies market entry for poor nation merchandise, whereas wealthy nations use assist as a lever to open poor nation markets to their merchandise
- Massive tasks or huge grand methods typically fail to assist the weak as cash can typically be embezzled away.
This text explores who has benefited most from this assist, the recipients or the donors.
On this web page:
- Governments Chopping Again on Promised Tasks
- International Help Numbers in Charts and Graphs
- Are numbers the one problem?
- Help as a overseas coverage software to help the donor not the recipient
- Help Quantities Dwarfed by Results of First World Subsidies, Third World Debt, Unequal Commerce, and many others
- However assist could possibly be useful
- Commerce and Help
- Bettering Financial Infrastructure
- Use assist to Empower, to not Prescribe
- Wealthy donor international locations and assist bureaucracies aren’t accountable
- Democracy-building is key, however more durable in lots of growing international locations
- Failed overseas assist and continued poverty: well-intentioned errors, calculated geopolitics, or a mixture?
Governments Chopping Again on Promised Tasks
Commerce, not assist
is thought to be an essential a part of growth promoted by some nations. However within the context of worldwide obligations, additionally it is criticized by many as an excuse for wealthy international locations to chop again assist that has been agreed and promised on the United Nations.
Wealthy Nations Agreed at UN to 0.7% of GNP To Help
The help is to return from the roughly 22 members of the OECD, often called the Improvement Help Committee (DAC). [Note that terminology is changing. GNP, which the OECD used up to 2000 is now replaced with the similar GNI, Gross National Income which includes a terms of trade adjustment. Some quoted articles and older parts of this site may still use GNP or GDP.]
ODA is principally assist from the governments of the rich nations, however doesn’t embody non-public contributions or non-public capital flows and investments. The principle goal of ODA is to advertise growth. It’s due to this fact a type of measure on the priorities that governments themselves placed on such issues. (Whether or not that essentially displays their citizen’s needs and priorities is a unique matter!)
Virtually all wealthy nations fail this obligation
Although these targets and agendas have been set, yr after yr nearly all wealthy nations have always failed to succeed in their agreed obligations of the 0.7% goal. As a substitute of 0.7%, the quantity of assist has been round 0.2 to 0.4%, some $150 billion brief annually.
Some donate many {dollars}, however are low on GNI %
Some attention-grabbing observations will be made concerning the quantity of assist. For instance:
- USA’s assist, by way of share of their GNP has nearly at all times been decrease than every other industrialized nation on this planet, although paradoxically since 2000, their greenback quantity has been the very best.
- Between 1992 and 2000, Japan had been the most important donor of assist, by way of uncooked {dollars}. From 2001 the USA claimed that place, a yr that additionally noticed Japan’s quantity of assist drop by almost 4 billion {dollars}.
Help growing since 2001 however nonetheless means beneath obligations
All through the Nineties, ODA declined from a excessive
of 0.33% of whole DAC assist in 1990 to a low of 0.22% in 1997. 2001 onwards has seen a pattern of elevated assist. Aspect ObserveThe UN famous the irony that the decline in assist got here at a time the place situations had been bettering for its higher effectiveness . In response to the World Financial institution, total, the official growth help worldwide had been lowering about 20% since 1990.
Between 2001 and 2004, there was a continuing improve in assist, however a lot of it because of geo-strategic considerations of the donor, corresponding to combating terrorism. Will increase in 2005 had been largely because of huge debt reduction for Iraq, Nigeria, plus another one-off giant gadgets.
(As will likely be detailed additional beneath, assist has usually adopted donor’s pursuits, not essentially the recipients, and as such the poorest haven’t at all times been the main focus for such assist. Moreover, the numbers, as little as they’re, are literally extra flattering to donor nations than they need to be: the unique definition of assist was by no means supposed to incorporate debt reduction or humanitarian emergency help, however as a substitute was meant for growth functions. That is mentioned additional beneath, too.)
International Help Numbers in Charts and Graphs
And who will get what?
Help cash is definitely means beneath what has been promised
Aspect be aware on non-public contributions
As an apart, it must be emphasised that the above figures are evaluating authorities spending. Such spending has been agreed at worldwide stage and is unfold over various priorities.
Particular person/non-public donations could also be focused in some ways. Nonetheless, despite the fact that the charts above do present US assist to be poor (in share phrases) in comparison with the remainder, the generosity of the American folks is much extra spectacular than their authorities. Personal assist/donation usually by means of the charity of particular person folks and organizations will be weighted to sure pursuits and areas. Nonetheless, it’s attention-grabbing to notice for instance, primarily based on estimates in 2002, Individuals privately gave no less than $34 billion abroad — greater than twice the US official overseas assist of $15 billion at the moment:
- Worldwide giving by US foundations: $1.5 billion per yr
- Charitable giving by US companies: $2.8 billion yearly
- American NGOs: $6.6 billion in grants, items and volunteers.
- Spiritual abroad ministries: $3.4 billion, together with well being care, literacy coaching, reduction and growth.
- US schools scholarships to overseas college students: $1.3 billion
- Private remittances from the US to growing international locations: $18 billion in 2000
- Supply: Dr. Carol Adelman, Help and Consolation, Tech Central Station, 21 August 2002.
Though Adelman admitted that there aren’t any full figures for worldwide non-public giving
she nonetheless claimed that Individuals are clearly essentially the most beneficiant on earth in public—however particularly in non-public—giving
. Whereas her assertions must be taken with warning, the numbers are excessive.
Rating the Wealthy primarily based on Dedication to Improvement
Personal donations and philanthropy
Authorities assist, whereas fraught with issues (mentioned beneath), displays overseas coverage goals of the donor authorities in energy, which may differ from the generosity of the folks of that nation. It may also be much less specialised than non-public contributions and targets are internationally agreed to be measurable.
Personal donations, particularly giant philanthropic donations and enterprise givings, will be topic to political/ideological or financial end-goals and/or topic to particular curiosity. A vivid instance of that is in well being points world wide. Amazingly giant donations by foundations such because the Invoice and Melinda Gates Basis are spectacular, however the underlying causes of the issues aren’t addressed, which require political options. As Rajshri Dasgupta feedback:
Personal charity is an act of privilege, it might probably by no means be a viable different to State obligations,mentioned Dr James Obrinski, of the organisation Medicins sans Frontier, in Dhaka not too long ago on the Folks’s Well being Meeting (see Himal, February 2001). In a nutshell, business and personal donations are feel-good, short-term interventions and no substitute for the vastly bigger, and primarily political, process of bringing well being care to greater than a billion poor folks.
As one other instance, Invoice Gates introduced in November 2002 an enormous donation of $100 million to India over ten years to struggle AIDS there. It was huge information and really welcome by many. But, on the identical time he made that donation, he was making one other bigger donation—over $400 million, over three years—to extend assist for Microsoft’s software program growth suite of purposes and its platform, in competitors with Linux and different rivals. Thomas Inexperienced, in a considerably cynical article, questions who actually advantages, saying And being a monster MS [Microsoft] shareholder himself, a
(Emphasis is authentic.)Large Win
in India will enrich him [Bill Gates] personally, maybe effectively in extra of the $100 million he’s donating to the AIDS downside. Makes you surprise who the actual beneficiary of charity is right here.
India has doubtlessly one tenth of the world’s software program builders, so capturing the market there of software program growth platforms is seen as essential. This is only one amongst many examples of what seems extraordinarily welcome philanthropy and charity additionally having different motives. It may be seen as horrible to criticize such charity, particularly on an important problem corresponding to AIDS, however that’s not the problem. The priority is that whereas it’s welcome that this charity is being offered, at a systemic stage, such charity is unsustainable and reveals ulterior motives. Would Invoice Gates have donated that a lot had there not been extra pursuits for the corporate that he had based?
As well as, as award-winning investigative reporter and creator Greg Palast additionally notes, the World Commerce Group’s Commerce-Associated Mental Property Rights (TRIPS), the rule which helps Gates rule, additionally bars African governments from shopping for AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis medication at low cost market costs.
He additionally provides that it’s killing extra folks than the philanthropy saving. What Palast is hinting in the direction of is the unequal guidelines of commerce and economics which might be a part of the world system, that has contributed to international locations corresponding to most in Africa being unable to handle the scourge of AIDS and different issues, even once they wish to. See for instance, the sections on free commerce, poverty and companies on this web page for extra.
The LA Occasions has additionally discovered that the Gates Basis has been investing in questionable corporations which might be typically concerned in environmental air pollution, even baby labor, and extra.
Along with non-public contributions, in the case of authorities assist, these considerations can multiply as it could have an effect on the financial and political route of a whole nation if such authorities assist can also be tied into political goals that profit the donor.
Are numbers the one problem?
As we are going to see additional beneath, some assist has certainly been fairly damaging for the recipient, whereas on the identical time being useful for the donor.
Help is Truly Hampering Improvement
See additionally, for instance, the well-regarded Actuality of Help challenge for extra on the truth and rhetoric of assist. This challenge appears at what varied nations have donated, and the way and the place it has been spent, and many others.
Personal flows typically don’t assist the poorest
Whereas ODA’s prime function is to advertise growth, non-public flows are sometimes considerably bigger than ODA. Throughout financial booms, extra funding is noticed in quickly rising economies, for instance. However this doesn’t essentially imply the poorest nations get such funding.
Throughout the increase of the mid-2000s earlier than the world monetary disaster sub-Saharan Africa didn’t appeal to as a lot funding from the wealthy nations, for instance (although when China determined to spend money on Africa, wealthy nations regarded on this suspiciously fearing exploitation, nearly ignoring their very own a long time of exploitation of the continent. China’s curiosity is no-doubt motivated by self-interest, and time must inform whether or not there may be certainly exploitation occurring, or if African nations will have the ability to demand honest situations or not).
As non-public flows to growing international locations from multinational corporations and funding funds mirror the pursuits of buyers, the significance of Abroad Improvement Help can’t be ignored.
Moreover, (and detailed beneath) these whole flows are lower than the subsidies lots of the wealthy nations give to a few of their industries, corresponding to agriculture, which has a direct influence on the poor nations (because of flooding the market with—or dumping—extra merchandise, defending their very own markets from the merchandise of the poor international locations, and many others.)
As well as, a variety of different inter-related points, corresponding to geopolitics, worldwide economics, and many others all tie into assist, its effectiveness and its function. Africa is usually highlighted as an space receiving extra assist, or in want of extra of it, but, lately, it has seen much less assist and fewer funding and many others, all of the whereas being subjected to worldwide insurance policies and agreements which have been detrimental to many African folks.
For the June 2002 G8 summit, a briefing was ready by Motion for Southern Africa and the World Improvement Motion, wanting on the wider problem of financial and political issues:
It’s simple that there was poor governance, corruption and mismanagement in Africa. Nonetheless, the briefing reveals the context—the legacy of colonialism, the assist of the G8 for repressive regimes within the Chilly Warfare, the creation of the debt lure, the large failure of Structural Adjustment Programmes imposed by the IMF and World Financial institution and the deeply unfair guidelines on worldwide commerce. The function of the G8 in creating the situations for Africa’s disaster can’t be denied. Its overriding duty should be to place its personal home so as, and to finish the unjust insurance policies which might be inhibiting Africa’s growth.
Because the above briefing is titled, a typical theme on these points (world wide) has been to blame the sufferer
. The above briefing additionally highlights some widespread myths
typically used to focus on such features, together with (and quoting):
- Africa has acquired growing quantities of assist through the years—in truth, assist to Sub-Saharan Africa fell by 48% over the Nineties
- Africa must combine extra into the worldwide financial system—in truth, commerce accounts for bigger proportion of Africa’s earnings than of the G8
- Financial reform will generate new overseas funding—in truth, funding to Africa has fallen since they opened up their economies
- Dangerous governance has prompted Africa’s poverty—in truth, in accordance with the UN Convention on Commerce and Improvement (UNCTAD), financial situations imposed by the IMF and the World Financial institution had been the dominant affect on financial coverage within the 20 years to 2000, a interval through which Africa’s earnings per head fell by 10% and earnings of the poorest 20% of individuals fell by 2% per yr
The amount problem is an enter into the help course of. The standard is concerning the output. We see from the above then, that the amount of assist has not been as a lot accurately. However what concerning the high quality of the help?
Help seems to have established as a precedence the significance of influencing home coverage within the recipient international locations
As proven all through this web page (and lots of of others) one of many root causes of poverty lies within the highly effective nations which have formulated a lot of the commerce and assist insurance policies right now, that are extra to do with sustaining dependency on industrialized nations, offering sources of low cost labor and cheaper items for populations again dwelling and growing private wealth, and sustaining energy over others in varied methods. As talked about within the structural adjustment part, so-called lending and growth schemes have achieved little to assist poorer nations progress.
The US, for instance, has additionally held again dues to the United Nations, which is the most important physique making an attempt to supply help in such a wide range of methods to the growing international locations. Former US President Jimmy Carter describes the US as stingy
:
Whereas the US offered giant quantities of navy assist to international locations deemed strategically essential, others famous that the US ranked low amongst developed nations within the quantity of humanitarian assist it offered poorer international locations.
We’re the stingiest nation of all,former President Jimmy Carter mentioned not too long ago in an deal with at Principia School in Elsah, Ailing.
Evan Osbourne, writing for the Cato Institute, additionally questioning the effectiveness of overseas assist and famous the pursuits of various different donor international locations, in addition to the U.S., of their assist methods in previous years. For instance:
- The US has directed assist to areas the place it has considerations associated to its nationwide safety, e.g. Center East, and in Chilly Warfare occasions specifically, Central America and the Caribbean;
- Sweden has targetted assist to
progressive societies
; - France has sought to advertise upkeep or protect and unfold of French tradition, language, and affect, particularly in West Africa, whereas disproportionately giving assist to those who have in depth business ties with France;
- Japan has additionally closely skewed assist in the direction of these in East Asia with in depth business ties along with situations of Japanese purchases;
Osbourne additionally added that home stress teams (company foyer teams, and many others) have additionally confirmed fairly adept at steering assist to their favored recipients.
And so, If assist will not be significantly given with the intention to foster financial progress, it’s maybe not stunning that it doesn’t obtain it.
Help Cash Typically Tied to Numerous Restrictive Situations
Of their 2000 report wanting again on the earlier yr, the Actuality of Help 2000 (Earthscan Publications, 2000, p.81), reported of their US part that 71.6% of its bilateral assist commitments had been tied to the acquisition of products and companies from the US.
That’s, the place the US did give assist, it was most frequently tied to overseas coverage goals that may assist the US.
Main as much as the UN Convention on Financing for Improvement in Monterrey, Mexico in March 2002, the Bush administration promised an almost $10 billion fund over three years adopted by a everlasting improve of $5 billion a yr thereafter. The EU additionally provided some $5 billion improve over the same time interval.
Whereas these will increase have been welcome, these targets are nonetheless beneath the 0.7% promised on the Earth summit in Rio de Janeiro in 1992. The World Financial institution have additionally leveled some criticism of previous insurance policies:
Commenting on the newest US pledge [of $10 billion], Julian Borger and Charlotte Denny of the Guardian (UK) say Washington is determined to deflect consideration in Monterrey from the scale of its assist price range. However for extra beneficiant donors, says the story, Washington’s conversion to the reason for efficient assist spending is tough to swallow. Among the many huge donors, the US has the worst file for spending its assist price range on itself—70 % of its assist is spent on US items and companies. And greater than half is spent in center earnings international locations within the Center East. Solely $3bn a yr goes to South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.
As well as, guarantees of extra money had been tied to extra situations, which for a lot of growing international locations is one other barrier to actual growth, because the situations are generally favorable to the donor, not essentially the recipient. Delhi-based Centre for Science and Atmosphere commented on the US conditional pledge of extra money that:
Thus, establishment in world relations is maintained. Wealthy international locations just like the US proceed to have a monetary lever to dictate what good governance means and to pry open markets of growing international locations for multinational companies. Creating international locations don’t have any such deal with for Northern markets, even in sectors like agriculture and textiles, the place they’ve a bonus however proceed to face commerce limitations and subsidies. The estimated annual price of Northern commerce limitations to Southern economies is over US $100 billion, way more than what growing international locations obtain in assist.
One other facet of assist tying into pursuits of donors is exemplified with local weather change negotiations. Highly effective nations corresponding to the USA have been vocally in opposition to the Kyoto Protocol on local weather change. Not like smaller international locations, they’ve been in a position to exert their affect on different international locations to push for bilateral agreements conditioned with assist, in a means that some would describe as a bribe. Heart for Science and Atmosphere for instance criticizes such politics:
It’s simple to be taken in with guarantees of bilateral assist, and make seemingly innocuous commitments in bilateral agreements. There may be far an excessive amount of at stake right here [with climate change]. To additional their pursuits, smaller, poorer international locations don’t have assist to bribe and commerce muscle to threaten international locations.
This use of energy in political and financial arenas is nothing new. Highly effective nations have at all times managed to exert their affect in varied arenas. Throughout the Gulf Warfare in 1991 for instance, many who ended up within the allied coalition had been promised varied concessions behind the scenes (what the media described as diplomacy
). For instance, Russia was provided huge IMF cash. Even now, with the problem of the Worldwide Legal Courtroom, which the US can also be against, it has been pressuring different nations on a person foundation to not signal, or present concessions. In that context, assist is usually tied to political goals and it may be tough to generally see when it isn’t so.
However some forms of situations hooked up to help may also be ideologically pushed. For instance, quoted additional above by the New York Occasions, James Wolfensohn, the World Financial institution president famous how European and American farm subsidies are crippling Africa’s likelihood to export its means out of poverty.
Whereas this criticism comes from many views, Wolfensohn’s be aware on export additionally means that some types of growth help could also be on the situation that nations reform their economies to sure ideological positions. Structural Adjustment has been considered one of these predominant insurance policies as a part of this neoliberal ideology, to advertise export-oriented growth in a quickly opened financial system. But, this has been probably the most disastrous insurance policies up to now 20 years, which has elevated poverty. Even the IMF and World Financial institution have hinted on occasion that such insurance policies aren’t working. Folks can perceive how tying assist on situation of bettering human rights, or democracy may be interesting, however when tied to financial ideology, which isn’t at all times confirmed, or not at all times following the one dimension matches all
mannequin, the power (and accountability) of selections that governments must pursue insurance policies they consider will assist their very own individuals are lowered.
Extra Cash Is Transferred From Poor Nations to Wealthy, Than From Wealthy To Poor
For the OECD international locations to fulfill their obligations for assist to the poorer international locations will not be an financial downside. It’s a political one. This may be seen within the context of different spending. For instance,
- The US not too long ago elevated its navy price range by some $100 billion {dollars} alone
- Europe subsidizes its agriculture to the tune of some $35-40 billion per yr, even whereas it calls for different nations to liberalize their markets to overseas competitors.
- The US additionally launched a $190 billion greenback subsidy to its farms by means of the US Farm Invoice, additionally criticized as a protectionist measure.
- Whereas assist quantities to round $70 to 100 billion per yr, the poor international locations pay some $200 billion to the wealthy annually.
- There are various extra (some talked about beneath too).
In impact then, there may be extra assist to the wealthy than to the poor.
Whereas the quantity of assist from some international locations such because the US would possibly look very beneficiant in sheer greenback phrases (ignoring the proportion problem for the second), the World Financial institution additionally identified that on the World Financial Discussion board in New York, February 2002, [US Senator Patrick] Leahy famous that two-thirds of US authorities assist goes to solely two international locations: Israel and Egypt. A lot of the remaining third is used to advertise US exports or to struggle a warfare in opposition to medication that might solely be received by tackling drug abuse in the USA.
In October 2003, at a United Nations convention, UN Secretary Common Kofi Annan famous that
growing international locations made the sixth consecutive and largest ever switch of funds to
different international locationsin 2002, a sum totallingnearly $200 billion.
Funds must be shifting from developed international locations to growing international locations, however these numbers inform us the other is going on…. Funds that must be selling funding and progress in growing international locations, or constructing faculties and hospitals, or supporting different steps in the direction of the Millennium Improvement Objectives, are, as a substitute, being transferred overseas.
And as Saradha Lyer, of Malaysia-based Third World Community notes, as a substitute of selling funding in well being, schooling, and infrastructure growth within the third world, this cash has been channelled to the North, both due to debt servicing preparations, asymmetries and imbalances within the commerce system or due to inappropriate liberalization and privatization measures imposed upon them by the worldwide monetary and buying and selling system.
This switch from the poorer nations to the wealthy ones makes even the current improve in ODA appear little compared.
Help Quantities Dwarfed by Results of First World Subsidies, Third World Debt, Unequal Commerce, and many others
Combining the above talked about reversal of flows with the subsidies and different distorting mechanisms, this all quantities to some huge cash being transferred to the richer international locations (also called the worldwide North), in comparison with the full assist quantities that goes to the poor (or South).
In addition to having a direct influence on poorer nations, it additionally impacts smaller farmers in wealthy nations. For instance, Oxfam, criticizing EU double requirements, highlights the next:
Latin America is the worst-affected area, dropping $4bn yearly from EU farm insurance policies. EU assist to agriculture is equal to double the mixed assist budgets of the European Fee and all 15 member states. Half the spending goes to the largest 17 per cent of farm enterprises, belying the manufactured fantasy that the CAP [Common Agriculture Policy] is all about protecting small farmers in jobs.
The double requirements that Oxfam mentions above, and that numerous others have highlighted has a big impact on poor international locations, who’re pressured to comply with liberalization and lowering authorities interference
whereas wealthy nations are in a position to subsidize a few of their industries. Poor international locations consequently have an excellent more durable time competing. IPS captures this effectively:
On the one hand, OECD international locations such because the US, Germany or France proceed by means of the ECAs [export credit agencies] to subsidise exports with taxpayers’ cash, typically in detriment to the competitiveness of the poorest international locations of the world,says [NGO Environment Defence representative, Aaron] Goldzimmer.Alternatively, the official growth help which is one technique to assist the international locations of the South to discover a sustainable path to growth and progress is being lowered.…
Authorities subsidies imply appreciable price discount for main corporations and quantity to round 10 per cent of annual world commerce. Within the yr 2000, subsidies by means of ECAs added as much as 64 billion {dollars} of exports from industrialised international locations, effectively above the official growth help granted final yr of 51.4 billion {dollars}.
In addition to agriculture, textiles and clothes is one other mainstay of many poor international locations. However, as with agriculture, the wealthier international locations have lengthy held up limitations to stop being out-competed by poorer nation merchandise. This has been achieved by means of issues like subsidies and varied agreements
. The influence to the poor has been far-reaching, as Buddies of the Earth highlights:
Regardless of the plain significance of the textile and clothes sectors by way of growth alternatives, the North has persistently and systematically repressed growing nation manufacturing to guard its personal home clothes industries.
Because the Seventies the textile and clothes commerce has been managed by means of the Multi-Fibre Association (MFA) which units bilateral quotas between importing and exporting international locations. This was supposedly to guard the clothes industries of the industrialised world whereas they tailored to competitors from growing international locations. Whereas there are instances the place such safety could also be warranted, particularly for transitionary intervals, the MFA has been in place since 1974 and has been prolonged 5 occasions. In response to Oxfam, the MFA is,
…essentially the most vital..[non tariff barrier to trade]..which has confronted the world’s poorest international locations for over 20 years.Though the MFA has been changed by the Settlement on Textiles and Clothes (ATC) which phases out assist over an extra ten yr interval—albeit by means of a course of which in itself is very inequitable—growing international locations are nonetheless struggling the results. The full price to growing international locations of restrictions on textile imports into the developed world has been estimated to be some $50 billion a yr. This is kind of equal to the full quantity of annual growth help offered by Northern governments to the Third World.
January 24, 2001
There may be typically a lot discuss of commerce moderately than assist, of growth, of opening markets and many others. However, when on the identical time a number of the essential markets of the US, EU and Japan seem like no-go areas for the poorer nations, then such discuss has been criticized by some as being hole. The New York Occasions is value quoting at size:
Our compassion [at the 2002 G8 Summit talking of the desire to help Africa] could also be effectively meant, however additionally it is hypocritical. The US, Europe and Japan spend $350 billion annually on agricultural subsidies (seven occasions as a lot as world assist to poor international locations), and this cash creates gluts that decrease commodity costs and erode the dwelling customary of the world’s poorest folks.
These subsidies are crippling Africa’s likelihood to export its means out of poverty,mentioned James Wolfensohn, the World Financial institution president, in a speech final month.Mark Malloch Brown, the pinnacle of the United Nations Improvement Program, estimates that these farm subsidies price poor international locations about $50 billion a yr in misplaced agricultural exports. By coincidence, that’s about the identical as the full of wealthy international locations’ assist to poor international locations, so we take again with our left hand each cent we give with our proper.
It’s holding down the prosperity of very poor folks in Africa and elsewhere for very slim, egocentric pursuits of their very own,Mr. Malloch Brown says of the wealthy world’s agricultural coverage.It additionally appears a tad hypocritical of us to complain about governance in third-world international locations after we enable tiny teams of farmers to hijack billion of {dollars} out of our taxes.
In truth, J. Brian Atwood, stepped down in 1999 as head of the US overseas assist company, USAID. He was very essential of US insurance policies, and vented his frustration that regardless of many well-publicized commerce missions, we noticed nearly no improve of commerce with the poorest nations. These nations couldn’t interact in commerce as a result of they might not afford to purchase something.
(Quoted from a speech that he delivered to the Abroad Improvement Council.)
As Jean-Bertrand Arisitde additionally factors out, there may be additionally a boomerang impact of loans as giant parts of assist cash is tied to purchases of products and commerce with the donor:
Many within the first world think about the amount of cash spent on assist to growing international locations is huge. In truth, it quantities to solely 0.3% of GNP of the industrialized nations. In 1995, the director of the US assist company defended his company by testifying to his congress that 84 cents of each greenback of assist goes again into the US financial system in items and companies bought. For each greenback the USA places into the World Financial institution, an estimated $2 really goes into the US financial system in items and companies. In the meantime, in 1995, severely indebted low-income international locations paid one billion {dollars} extra in debt and curiosity to the Worldwide Financial Fund (IMF) than they acquired from it. For the 46 international locations of Subsaharan Africa, overseas debt service was 4 occasions their mixed governmental well being and schooling budgets in 1996. So, we discover that assist doesn’t assist.
In different phrases, typically assist doesn’t assist the recipient, it aids the donor. For the US within the above instance, its assist company has been a overseas coverage software to boost its personal pursuits, efficiently.
After which there was the disastrous meals assist insurance policies, which is one other instance of offering assist however utilizing that assist as an arm of overseas coverage goals. It has helped their companies and huge farmers at an enormous price to growing international locations, and has seen a rise in starvation, not discount. For extra particulars, see the whole part on this web site that discusses this, within the Poverty and Meals Dumping a part of this web page.
For the world’s hungry, nonetheless, the issue isn’t the stinginess of our assist. When our ranges of help final boomed, beneath Ronald Reagan within the mid-Eighties, the emphasis was hardly on eliminating starvation. In 1985, Secretary of State George Shultz said flatly that
our overseas help applications are very important to the achievement of our overseas coverage targets.However Shultz’s assertion shouldn’t shock us. Each nation’s overseas assist is a software of overseas coverage. Whether or not that assist advantages the hungry is decided by the motives and targets of that coverage—by how a authorities defines the nationwide curiosity.
The above quote from the ebook World Starvation is from Chapter 10, which can also be reproduced in full on this web page. It additionally has extra info and stats on US assist and overseas coverage goals, and many others.
As an apart, it’s attention-grabbing to notice the disparities between what the world spends on navy, in comparison with different worldwide obligations and commitments. Most rich nations spend far extra on navy than growth, for instance. The United Nations, which will get its monies from member nations, spends about $10 billion—or about 3% of what simply the US alone spends on its navy. It’s going through a monetary disaster as international locations such because the US wish to cut back their burden of the prices—which comparatively is kind of low anyway—and have tried to withhold funds or continued in accordance with varied extra situations.
And with the current monetary disaster, clearly the act of getting sources collectively will not be the problem, as way more has been made out there in only a few brief months than a whole 4 a long time of assist:
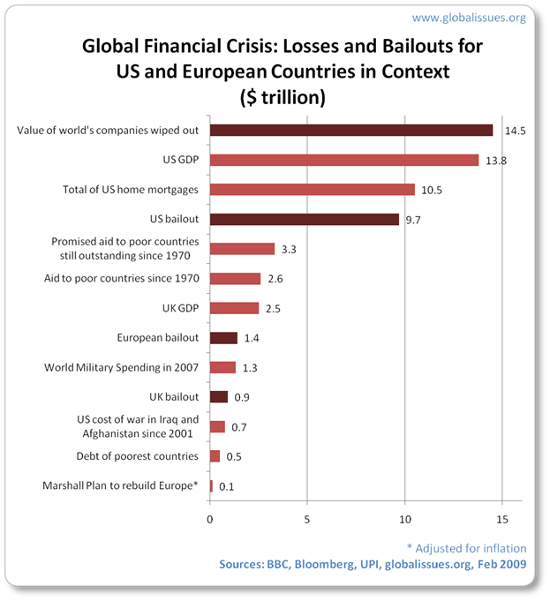
However, because the quote above highlights as effectively, in addition to the quantity of assist, the high quality of assist is essential. (And the above highlights that the standard has not been good both.)
However assist could possibly be useful
Authorities assist, from the USA and others, as indicated above can typically fall foul of political agendas and pursuits of donors. On the identical time that’s not the one assist going to poor international locations. The US itself, for instance, has a protracted custom of encouraging charitable contributions. Certainly, tax legal guidelines within the US and varied European international locations are favorable to such giving as mentioned additional above. However non-public funding, philanthropy and different sources of assist can even fall foul of comparable or different agendas, in addition to problems with focus on some areas over others, of accountability, and so forth. (Extra on these features is launched on this web site’s NGO and Improvement part.)
Commerce and Help
Oxfam highlights the significance of commerce and assist:
Some Northern governments have burdened that
commerce not assistmust be the dominant theme on the [March 2002 Monterrey] convention [on Financing for Development]. That strategy is disingenuous on two counts. First, wealthy international locations have didn’t open their markets to poor international locations. Second, elevated assist is important for the world’s poorest international locations if they’re to understand the alternatives offered by means of commerce.
Along with commerce not assist
views, the Bush Administration was eager to push for grants moderately than loans from the World Financial institution. Grants being free cash seems to be extra welcome, although many European nations aren’t as happy with this selection. Moreover, some commentators level out that the World Financial institution, being a Financial institution, shouldn’t give out grants, which might make it compete with different grant-offering establishments corresponding to varied different United Nations our bodies. Additionally, there may be concern that it could be simpler to impose political situations to the grants. John Taylor, US Undersecretary of the Treasury, in a current speech in Washington additionally identified that Grants aren’t free. Grants will be simply be tied to measurable efficiency or outcomes.
Some remark that maybe grants might result in extra dependencies in addition to some nations might conform to much more situations whatever the penalties, as a way to get the free cash. (Extra about the problem of grants is mentioned by the Bretton Woods Venture.)
In discussing commerce insurance policies of the US, and EU, in relation to its results on poor international locations, chief researcher of Oxfam, Kevin Watkins, has been very essential, even charging them with hypocrisy for preaching free commerce however working towards mercantilism:
Wanting past agriculture, it’s tough to keep away from being struck by the discrepancy between the image of US commerce coverage painted by [US Trade Representative, Robert] Zoellick and the realities going through growing international locations.
To take one instance, a lot has been made from America’s generosity in the direction of Africa beneath the Africa Development and Alternative Act (AGOA). This gives what, on the floor, appears like free market entry for a spread of textile, garment and footwear merchandise. Scratch the floor and also you get a unique image. Beneath AGOA’s so-called rules-of-origin provisions, the yarn and material used to make attire exports should be made both in the USA or an eligible African nation. If they’re made in Africa, there’s a ceiling of 1.5 per cent on the share of the US market that the merchandise in query can account for. Furthermore, the AGOA’s protection is lower than complete. There are some 900 tariff traces not lined, for which common tariffs exceed 11%.
In response to the Worldwide Financial Fund (IMF), the advantages accruing to Africa from the AGOA can be some $420m, or 5 occasions, higher if the US eliminated the rules-of-origin restrictions. However these restrictions mirror the realities of mercantilist commerce coverage. The underlying precept is which you could export to America, offered that the export in query makes use of American merchandise moderately than these of opponents. For a rustic supposedly main a campaign for open, non-discriminatory world markets, it’s a curiously anachronistic strategy to commerce coverage.
Watkins lists various different areas, apart from the AGOA which might be beset with issues of hypocrisy, and concludes that nihilism and blind pursuit of US financial and company particular curiosity represents an impediment to the creation of a world buying and selling system able to extending the advantages of globalisation to the world’s poor.
(See additionally this web site’s part on free commerce and globalization, the place there may be extra criticism about northern international locations exhibiting mercantilist, or monopoly capitalist rules, moderately than free market capitalism, despite the fact that that’s what is preached to the remainder of the world.)
In that context then, and given the issues talked about additional above about agricultural and textiles/clothes subsidies, and many others. the present quantity of assist given to poor international locations doesn’t examine to assist
given to wealthier international locations’ companies and industries and hardly compensates for what’s misplaced.
Each growing and restructuring assist to really present growing international locations the instruments and means to develop for themselves, for instance, would assist recipients of assist, not simply the donors. Help is extra than simply charity and can’t be separated from different problems with politics and economics, which should even be thought of.
Bettering Financial Infrastructure
Commerce not Help
seems like respectable rhetoric. Because the economist Amartya Sen for instance says, loads that may be achieved at a comparatively little price. Sadly, to this point, plainly rhetoric is generally what it has turned out to be.
As well as, as J.W. Smith additional qualifies, moderately than giving cash that may be squandered away, maybe the very best type of assist can be business, straight:
Do Not Give the Needy Cash: Construct Them Industries As a substitute
With the file of corruption inside impoverished international locations, folks will query giving them cash. That may be dealt with by giving them the business straight, not the cash. To construct a balanced financial system, present client shopping for energy, and develop arteries of commerce that may soak up the manufacturing of those industries, contractors and labor in these international locations must be used. Legitimacy and safety of contracts is the premise of any sound financial system. Engineers know what these prices must be and, if price overruns begin coming in, the contractor who has confirmed incapable must be changed—simply as any good contract would require…. When offered the business, versus the cash to construct business, these folks can have bodily capital. The one income to be made then are in manufacturing; there isn’t any growth cash to intercept and ship to a Swiss checking account.
on-line)
Whether or not the hope for efficient overseas assist will really flip into actuality is more durable to know, due to energy politics, which has characterised and formed the world for hundreds of years.
A danger for growing international locations that look to help, no less than of their short-term plans to kick-start growth (for changing into depending on assist over the long term appears a harmful path to comply with), is that individuals of the wealthy world will see the failures of assist with out seeing the detailed explanation why, making a backlash of donor fatigue, reluctance and cynicism.
Writer and Web page Data
- Created:
- Final up to date:
[ad_2]
